91% of cyber attacks start with an email
Email is the most common type of threat vector, and 23% of people click on malicious emails. It only takes one click for your whole network to be...
2 min read
Harry | Junior SOC Analyst : Oct 10, 2022 4:42:22 PM

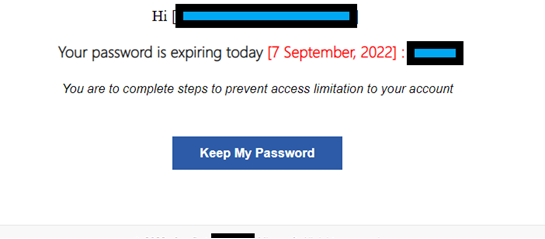
On the 7th of September 2022, we detected a new interesting technique used by a phishing attack to attempt to avoid URL scanning-based detection methods by redirecting to a random Wikipedia page. On the surface, the email seems like a generic password expiry phishing attempt which tries to convince the user that their password is expiring on that day and requests they access the link in the email.
This link is formatted as follows, “hxxp://COMPANYNAME[.]chasingpostcards[.]com/cGhpc2hpbmdAYXR0YWNrLmNvbQ==”. In the URL path a base 64 encoded email address is provided, in the URL example above the decoded address is “phishing@attack.com” which is used to format the phishing pages layout when a user clicks their customised link.
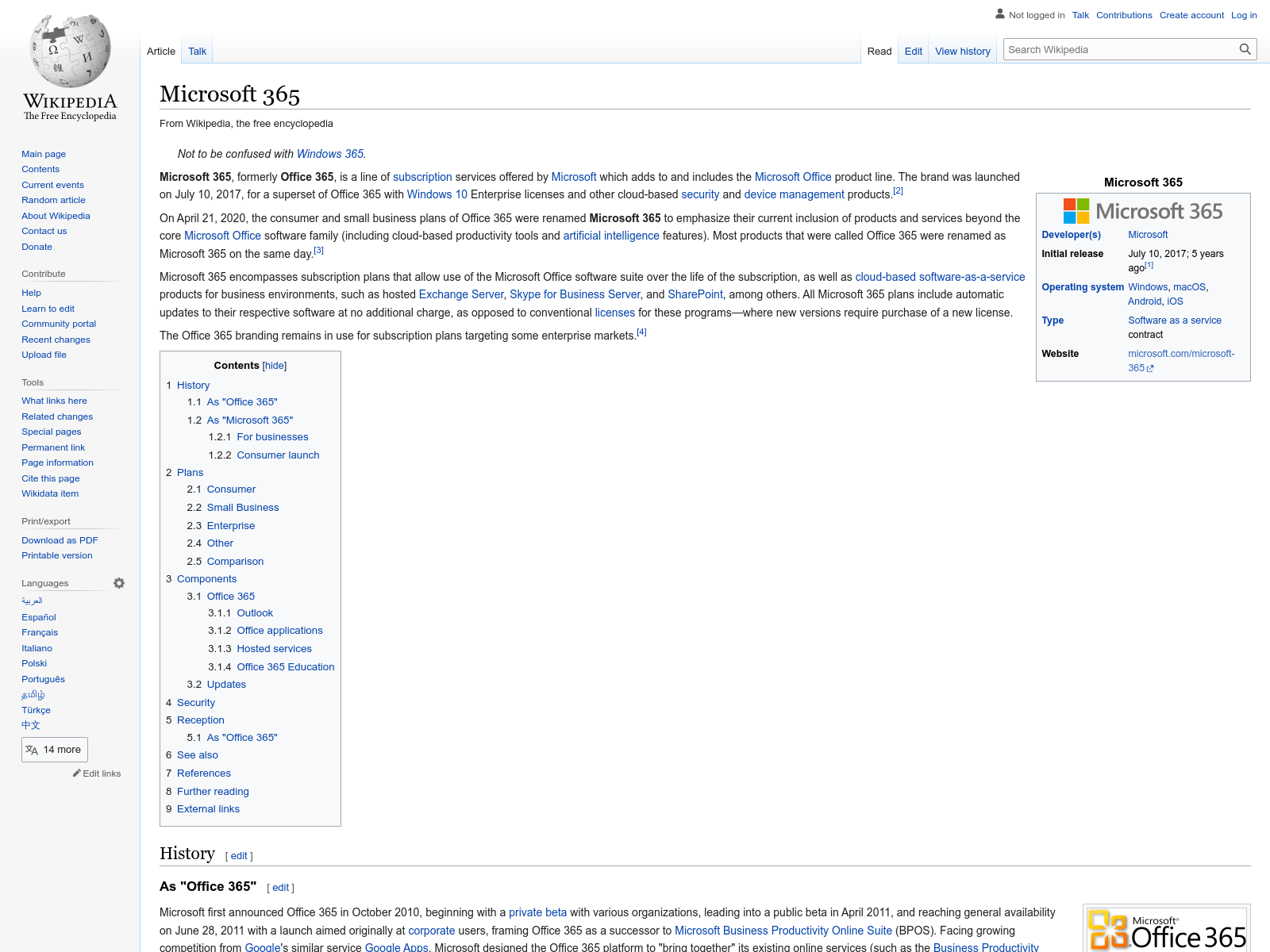
Using a URL scanning service on the “hxxp://COMPANYNAME[.]chasingpostcards[.]com/cGhpc2hpbmdAYXR0YWNrLmNvbQ==” URL, we can see that the chasingpostcards website redirects to a Microsoft related Wikipedia page such as "https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Microsoft_365." The chasingpostcards link will redirect to Wikipedia if scanned by an automated URL scanner, this is a method of avoiding detection as if a URL scanner cannot access the intended phishing page it will not report back that the links are suspicious.
Interestingly when accessing the “hxxp://COMPANYNAME[.]chasingpostcards[.]com/cGhpc2hpbmdAYXR0YWNrLmNvbQ==” link from a local sandboxed environment, we get redirected to “hxxp://moneypro[.]in/O/ cGhpc2hpbmdAYXR0YWNrLmNvbQ==” a page containing a reCAPTCHA which is used to prevent bots from accessing the fake M365 phishing page.
The chasingpostcards address is used as a gateway to prevent detection by automated scanning tools, we believe this to use various methods to define whether the access is a “legitimate” user or a scanner such as browser fingerprinting and IP address lookup.

After completing the captcha, we are greeted with a fake M365 phishing page.
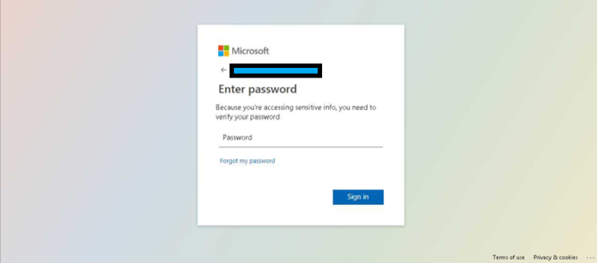
On this fake M365 login page there is a JavaScript script that can detect any user input without them clicking sign in. This method could capture a user’s passwords if they were to input the password into the field and then realise the site is not legitimate without clicking sign in. This could lead the targeted user to think they are safe and not compromised because they did not click sign in however this is not the case.
Our MDR for Email service was able to detect this using a multitude of signals. For example, the language used in the email, was similar to the language of other Credential Theft emails, the SMTP server’s IP address was also marked as suspicious due to being associated with other emails that were marked as phishing by other Analysts on our service. Finally, the email address sender name is similar to a sender name already in the targeted user's contacts.
Explore our MDR for email services.

Email is the most common type of threat vector, and 23% of people click on malicious emails. It only takes one click for your whole network to be...

The gangs behind ransomware attacks

What to do if you fall victim to a cyberattack